




Objectives:
=> To understand algebraically and graphically exponential and logarithms.
=> To understand and use linear (Cartesian) and semi-log graph paper for the representation of data.
=> To review differential and integral calculus
=> To understand and use spreadsheets
=> To understand the theory, instrumentation and application of spectrophotometric methods of analysis
Defn: N = bx or N = b^x
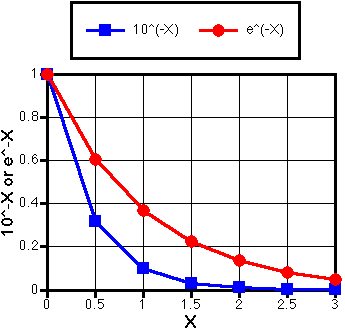
Figure II-1
Note use of ^
N is the number, b is the base, often 10 but also e ( = 2.7183), and x is the exponent
With common base, exponents can be added or subtracted
e.g. ax * ay = a(x+y) to perform multiplication or division.
Table II-1
|
|
0.0 |
0.5 |
1.0 |
1.5 |
2.0 |
2.5 |
3.0 |
|
1 0-x |
1.000 |
0.316 |
0.100 |
0.032 |
0.010 |
0.003 |
0.001 |
|
e-x |
1.000 |
0.607 |
0.368 |
0.223 |
0.135 |
0.082 |
0.050 |
Copyright 2001 David W.A. Bourne




