PHAR 4634 Fall 1995
Pharmaceutics III
OU HSC College of Pharmacy
Final Exam
14 December 1995
Section ONE. Sketch a Graph or Diagram - 8 x 3 = 24 points
Sketch the graphs or diagrams requested in the space provided.
Make sure you carefully include any distinguishing characteristics.
Assume that a linear one compartment model applies for each sketch
unless otherwise specified. Don't forget to include labels and units
for each axes of a graph.
Q 1.1 Sketch the components of the G.L.C. assay method. Label
three components.
3" x 2.5" space for sketch
Answer
Q 1.2 Draw a diagram showing the components of a linear two
compartment model after an IV bolus dose. Give the differential
equation for the plasma compartment.
3" x 2.5" space for sketch
Answer
Q 1.3 Linear plot of Cp versus time after an IV infusion for 3
hours, show Cp versus time for 12 hours.
3" x 2.5" space for sketch
Answer
Q 1.4 A Scatchard plot representing 1:1 drug protein binding with
one type of binding site.
3" x 2.5" space for sketch
Answer
Q 1.5 Sketch a simplified model of a biological membrane
3" x 2.5" space for sketch
Answer
Q 1.6 Sketch a linear graph of effective t50% versus log(Dose) for
a drug which is eliminated by two pathways; one a linear pathway and
the other saturable.
3" x 2.5" space for sketch
Answer
Q 1.7 Semi-log plot of Cp versus time after a 2 hour IV infusion
for a drug which exhibits two-compartment pharmacokinetics. Show Cp
for 12 hours.
3" x 2.5" space for sketch
Answer
Q 1.8 Sketch the components used in the beaker laboratory
experiment representing multiple IV bolus dosing.
3" x 2.5" space for sketch
Answer
Section TWO. True/False - Check the Correct Response. 8 x 2 = 16
points
Q 2.1 The E.M.I.T. assay method uses an enzyme-substrate reaction
as the means of quantitating drug concentrations. True False
Answer
Q 2.2 The types of detectors used with H.P.L.C. include FID, EC,
and MS. True False
Answer
Q 2.3 Appropriate units for AUMC are
amount.volume-1.time2. True False
Answer
Q 2.4 Elimination of salicylate, a weak acid, is faster when the
urine pH is 7.5 compared with when the urine pH is 8.5. True
False
Answer
Q 2.5 Phase II metabolism processes commonly result in metabolites
which have smaller molecular weight than the parent drug. True
False
Answer
Q 2.6 The parameter MAT has the units of time-1.
True False
Answer
Q 2.7 For a drug like phenytoin which exhibits Michaelis-Menten
elimination kinetics, when Km is much lower than plasma
concentrations elimination will appear to follow first order kinetics
True False
Answer
Q 2.8 A drug will tend to be extensively removed by hemodialysis
if it has good water solubility and is highly bound to plasma
protein. True False
Answer
Section THREE Calculations 10 + 14 + 12 + 16 + 8 = 60 points
Show all your work for full credit. All material not deleted or
crossed-out will be considered for grading.
Q 3.1 (10 points) A drug was given to a number of subjects
by a single IV bolus dose (250 mg) and then as a single oral dose
(400 mg), after a suitable wash-out period. The average data are
presented below. Complete the tables and calculate MRT(IV),
MRT(PO), MAT, and the absolute bioavailability of the oral dosage
form.
|
Time (hr)
|
Concentration (mg/L)
|
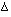 AUC AUC
|
AUC
|
Time (hr)
|
Cp*t
|
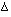 AUMC AUMC
|
AUMC
|
|
0
|
13.51
|
0.00
|
0.00
|
0
|
0.00
|
0.00
|
0.00
|
|
0.5
|
11.75
|
6.32
|
6.32
|
0.5
|
5.87
|
1.47
|
1.47
|
|
1
|
10.21
|
|
|
1
|
10.21
|
4.02
|
5.49
|
|
2
|
7.72
|
|
|
2
|
15.44
|
12.83
|
18.32
|
|
4
|
4.41
|
12.13
|
|
4
|
17.64
|
33.07
|
|
|
6
|
2.52
|
6.93
|
|
6
|
|
|
|
|
9
|
1.09
|
5.41
|
|
9
|
9.79
|
|
|
|

|
0.00
|
3.88
|
|

|
0.00
|
48.82
|
|
|
Time (hr)
|
Conc (mg/L)
|
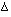 AUC AUC
|
AUC
|
Time (hr)
|
Cp*t
|
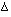 AUMC AUMC
|
AUMC
|
|
0
|
0.00
|
0.00
|
0.00
|
0
|
0.00
|
0.00
|
0.00
|
|
0.5
|
10.84
|
|
|
0.5
|
5.42
|
1.36
|
1.36
|
|
1
|
13.72
|
|
|
1
|
|
|
|
|
2
|
12.53
|
13.13
|
|
2
|
25.06
|
19.39
|
|
|
4
|
7.47
|
20.00
|
|
4
|
29.87
|
54.93
|
|
|
6
|
4.27
|
|
|
6
|
|
|
|
|
9
|
1.84
|
9.18
|
|
9
|
16.60
|
63.37
|
|
|

|
0.00
|
6.59
|
|

|
0.00
|
82.83
|
|
|
MRT(IV)
|
<-------->
|
<-------->
|
|
MRT(PO)
|
|
|
|
MAT
|
|
|
|
F
|
|
|
Answer
Q 3.2 (14 points) A 200 mg dose IV bolus dose was given to
a subject. After 8 hours another IV bolus dose of 150 mg was
administered. Twelve hours after the first IV bolus dose an IV
infusion of 40 mg/hr was started. If the elimination rate constant is
0.12 hr-1 and the apparent volume of distribution is 37 L,
calculate the plasma concentration 2 hours after the IV infusion was
started.
|
<------->
|
<------->
|
<------->
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Answer
Q 3.3 (12 points) A 40 year old man (80 kg) is to be
started on phenytoin once a day. He was initially given 375 mg/day
for two weeks. A plasma concentration was collected and measured at
12.9 mg/L. The dose was increased to 425 mg/day and another sample
was collected after a further two weeks. This time the concentration
was 20.4 mg/L. Calculate the Vm and Km value for this patient and a
suitable daily dose to achieve a plasma concentration as close as
possible to 15 mg/L. The only available capsule sizes are 25, 50,
100, and 250 mg. Calculate the expected plasma concentration.
|
<------->
|
<------->
|
<------->
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Answer
Q 3.4 (16 points) A drug was given by IV bolus (300 mg) and
the following data were collected. Calculate A, B,  ,
,  , k12, k21, kel,
V1 and Varea. Label and give units for the graph axes.
, k12, k21, kel,
V1 and Varea. Label and give units for the graph axes.
|
Time (hr)
|
Concentration (mg/L)
|
<---------->
|
<---------->
|
<---------->
|
|
0
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.25
|
15.0
|
|
|
|
|
0.5
|
12.5
|
|
|
|
|
0.75
|
10.5
|
|
|
|
|
1
|
9.0
|
|
|
|
|
2
|
5.9
|
|
|
|
|
3
|
4.5
|
|
|
|
|
4
|
3.6
|
|
|
|
|
6
|
2.4
|
|
|
|
|
9
|
1.3
|
|
|
|
|
12
|
0.7
|
|
|
|
|
<------->
|
<------->
|
<------->
|
|
A
|
|
|
|
B
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
k21
|
|
|
|
k12
|
|
|
|
kel
|
|
|
|
V1
|
|
|
|
Varea
|
|
|
Three cycle semi-log graph paper provided
Answer
Q 3.5 (8 points) Calculate an IV bolus loading dose and an
IV maintenance infusion for a 45 year old (78 kg) male patient
(height 6'0") to rapidly reach and maintain a plasma concentration of
20 mg/L. Assume a linear one compartment pharmacokinetic model with
t1/2 = 5.7 hr and V = 0.25 L/kg.
Answer
Exam Equations in PDF or html format
![]() AUC
AUC
![]() AUMC
AUMC
![]()
![]()