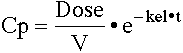 and the
superposition principle.
and the
superposition principle.1. Calculate Cp at 1, 2, 4, 6, 9, 12, 18, and 24 hours after 400 mg at 0 hr, 200 mg at 4 hr, and 300 mg at 12 hours. Use kel = 0.14 hr-1 and V = 54 L.
Use the equation:
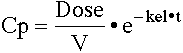 and the
superposition principle.
and the
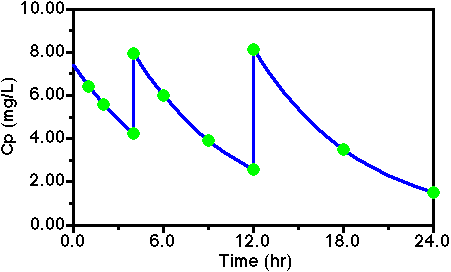
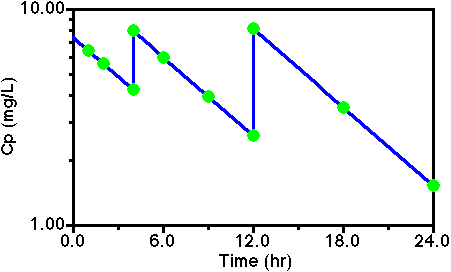
superposition principle.The concentration immediately after the first dose is Dose/V = 400/54 = 7.41 mg/L. After one hour this concentration falls to 7.41 x e-0.14 x 1 = 6.44 mg/L. After two hours Cp = 7.41 x e-0.14 x 2 = 5.60 mg/L and after 4 hours Cp = 7.41 x e-0.14 x 4 = 4.23 mg/L. After the second dose Cp = 4.23 + 200/54 = 7.93 mg/L. Two hours later, at 6 hr, Cp = 7.93 x e-0.14 x 2 = 6.00 mg/L and at 9 hours, 5 hours later, Cp = 7.93 x e-0.14 x 5 = 3.94 mg/L. Just before the third dose, at 12 hours, 8 hours after the second dose, Cp = 7.93 x e-0.14 x 8 = 2.59 mg/L. After the third dose Cp = 2.59 + 300/54 = 8.14 mg/L. At 18 and 24 hours, Cp = 8.14 x e-0.14 x 6 = 3.52 mg/L and Cp = 8.14 x e-0.14 x 12 = 1.52 mg/L.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. Calculate a dosing regimen for a male patient, age 56 ys and wt 86 kg with serum creatinine = 1.6 mg/100 ml. Previous studies with this drug indicate that kel = 0.04 hr-1 in patient with a creatinine clearance of 15 ml/min and kel = 0.14 hr-1 in patients with creatinine clearance of 60 ml/min and V = 0.78 L/kg. Graph the kel versus creatinine clearance data (on linear graph paper) to get a value for knr and slope.
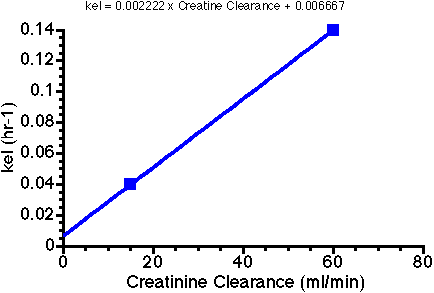
Thus knr = 0.006667 and slope = 0.002222.
Using the Cockcroft-Gault equation
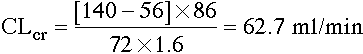
Thus
R = Cpmin/Cpmax = 0.5/6 = 0.08333 = e-0.146 x tau. Rearranging gives tau = 17.0 hr. Expanding tau to allow Cpmax and Cpmin to stay below 6 and 0.5 mg/L, respectively, gives 18 hours. The new R = e-0.146 x 18 = 0.07222. A loading dose can be calculated as L.D. = Cpmax x V = 6 x 0.78 x 86 = 402 -> 400 mg. The maintenance dose is Cpmax x V x (1- R) = L.D. x (1 - R) = 402 x (1 - 0.07222) = 373 -> 370 mg every 18 hours.
On-line Cpmax/Cpmin calculator
Using a loading dose of 400 mg should provide a Cp0 = Dose/V = 400/(0.78 x 86) = 5.96 mg/L.
The maintenance dose of 370 mg every 18 hours should provide a Cpmax value of MD/(V*(1-R)) = 370/((0.78 x 86) x (1 - 0.07222)) = 370/(67.1 x 0.928) = 5.94 mg/L. The expected Cpmin would be Cpmax*R = 5.94 x 0.07222 = 0.429 mg/L.
3. Calculate the oral dose required to achieve an average concentration of 20 mg/L. Given data: F = 0.75, t1/2 = 17 hr (i.e. kel = 0.0408 hr-1), V = 42 L, tau = 12 hr.
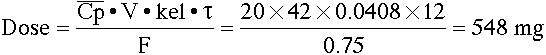
On-line Cp(average) calculator
Round the dose to 550 mg every 12 hours.
The average concentration is now F*Dose/(V*kel*tau) = 0.75 x 550/(42 x 0.0408 x 12) = 20.1 mg/L.
Since we don't have a value for ka and assuming that dose are given well separated we can use the equation Cpmin = (F*Dose/V)*(R/(1 - R)) = (0.75*550/42)*(exp(-0.0408*12)/(1-exp(-0.0408*12))) = 9.821 x (0.6129/(1 - 0.6129)) = 9.821 x 1.583 = 15.5 mg/L
Given that Cp(average) - Cpmin = 20.1 - 15.5 = 4.6 the estimated Cpmax would be 20.1 + 4.6 = 24.7 mg/:L. (Using Cpmin/Cpmax = R or Cpmax = Cpmin/R = 15.5/0.6129 = 25.3 mg/L).