return to the Course index
previous | next

redrawn from Cadwallader, 1983
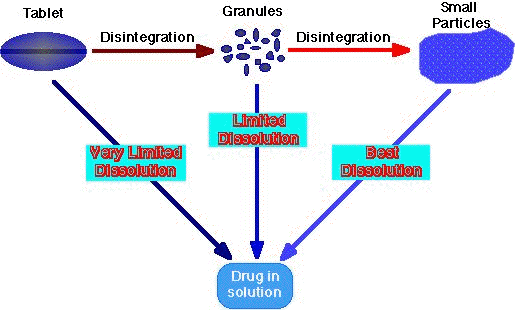
Fig 3.14.1 Slide showing the processes involved in the dissolution of a tablet before absorption. A drug cannot be absorbed across the intestinal wall as a solid. It must first dissolve in the fluid of the G-I tract. Tablets are carefully formulated, designed, to stay together in the bottle during transport but break up quickly once they are in an aqueous environment. This can be an easy or difficult job depending on the drug and the dose required. There are therefore dissolution tests specified to ensure that tablet formulations work. Also it may be appropriate to conduct experiments with human volunteers to ensure that the tablet does release the drug as it should.
Material on this website should be used for Educational or Self-Study Purposes Only
Copyright © 2001 - 2026 David W. A. Bourne (david@boomer.org)
 |
The Book Pharmacokinetics This Course in ePub format |
 |