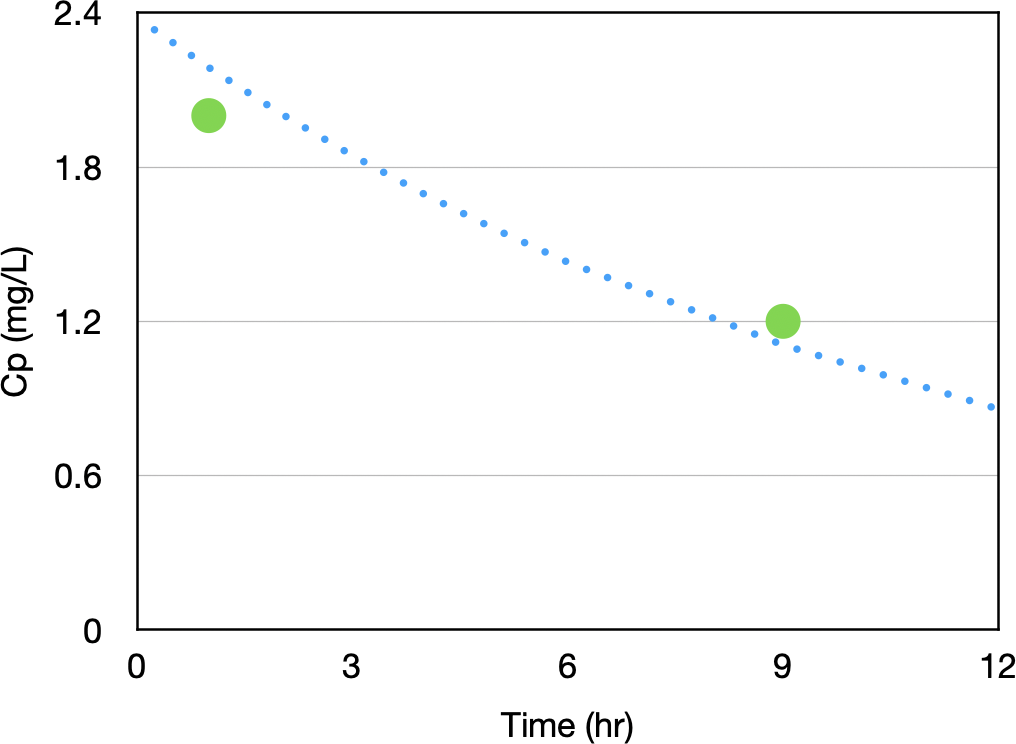
Figure 29.9.1 Simulated Concentration Time Data with Two Data Points
return to the Course index
previous | next

Figure 29.9.1 Simulated Concentration Time Data with Two Data Points
Combining these data points with our prior information about the pharmacokinetic model and model parameters we can perform a Bayesian analysis of the data.
Enter type# for parameter 1 (-5 to 51) 1
Enter parameter name Dose
Enter Dose value 100
0) fixed, 1) adjustable, 2) single dependence
or 3) double dependence 0
Enter component to receive dose 1
Enter component for F-dependence ( 1 to - 1 or 0 for no dependence)
Input summary for Dose (type 1)
Fixed value is 100.0
Dose/initial amount added to 1
Enter 0 if happy with input, 1 if not, 2 to start over
Enter -3 to see choices, -1 or -4 (save model) to exit this section
Enter type# for parameter 2 (-5 to 51) 2
Enter parameter name kel
Enter kel value 0.085
0) fixed, 1) adjustable, 2) single dependence
or 3) double dependence 1
Enter lower limit 0
Enter upper limit 1
Enter mean parameter value 0.085
Enter standard deviation 0.025
Enter component to receive flux 0
Enter component to lose flux 1
Input summary for kel (type 2)
Initial value 0.8500E-01 float between 0.000 and 1.000
Population mean 0.8500E-01 with std-dev 0.2500E-01
Transfer from 1 to 0
Enter 0 if happy with input, 1 if not, 2 to start over
Enter -3 to see choices, -1 or -4 (save model) to exit this section
Enter type# for parameter 3 (-5 to 51) 18
Enter parameter name V
Enter V value 42
0) fixed, 1) adjustable, 2) single dependence
or 3) double dependence 1
Enter lower limit 1
Enter upper limit 100
Enter mean parameter value 42
Enter standard deviation 17
Enter data set (line) number 1
Enter line description Cp
Enter component number (0 for obs x) 1
Input summary for V (type 18)
Initial value 42.00 float between 1.000 and 100.0
Population mean 42.00 with std-dev 17.00
Component 1 added to line 1
Enter 0 if happy with input, 1 if not, 2 to start over
Enter -3 to see choices, -1 or -4 (save model) to exit this section
Enter type# for parameter 4 (-5 to 51) -1
The results of this analysis are shown in Figure 22.3.4
** FINAL PARAMETER VALUES ***
# Name Value S.D. C.V. % Lower <-Limit-> Upper
Population mean S.D. (Weight) Weighted residual
1) kel 0.84658E-01 0.208E-02 2.5 0.0 1.0
0.8500E-01 0.2500E-01 40.00 -0.1369E-01
2) V 42.175 1.25 3.0 1.0 0.10E+03
42.00 17.00 0.5882E-01 0.1030E-01
Final WSS = 0.143082E-01 R^2 = 1.000 Corr. Coeff = 1.000
AIC = -4.49385 AICc = 0.00000
Log likelihood = 2.10 Schwarz Criteria = -7.10755
R^2 and R - jp1 1.000 1.000
R^2 and R - jp2 0.8809 0.9386
RMSE = 0.1425 or 8.371 % RMSE
MAE = 0.1359 ME = 0.4267E-01
Model and Parameter Definition
# Name Value Type From To Dep Start Stop
1) Dose = 100.0 1 0 1 0 0 0
2) kel = 0.8466E-01 2 1 0 0 0 0
3) V = 42.18 18 1 1 0 0 0
Data for Cp :-
DATA # Time Observed Calculated (Weight) Weighted residual
1 1.000 2.00000 2.17860 0.500000 -0.892979E-01
2 9.000 1.20000 1.10674 0.833333 0.777201E-01
iBook and pdf versions of this material and other PK material is available
Copyright © 2001-2022 David W. A. Bourne (david@boomer.org)