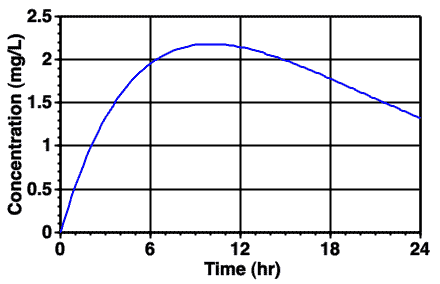
Figure 7.3.1 Typical Plot of Cp versus Time after Buccal Administration
return to the Course index
previous | next
Advantages:
First pass - The liver is by-passed thus there is no loss of drug by first pass effect for buccal or sublingual administration. Bioavailability is higher.
Rapid absorption - Because of the good blood supply to the area of absorption is usually quite rapid, especially for drugs with good lipid solubility.
Drug stability - pH in mouth relatively neutral (cf. stomach - acidic). Thus a drug may be more stable.
Disadvantages:
Holding the dose in the mouth is inconvenient. If any part of the dose is swallowed that portion must be treated as an oral dose and subject to first pass metabolism.
Usually more suitable for drugs with small doses.
Drug taste may need to be masked.

Figure 7.3.1 Typical Plot of Cp versus Time after Buccal Administration
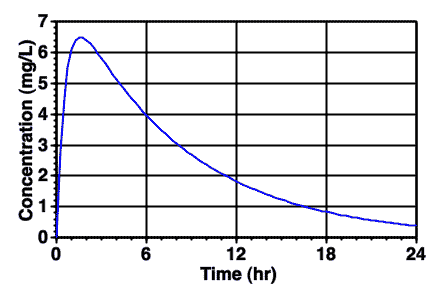
Figure 7.3.2 Typical Plot of Cp versus Time after Sublingual Administration
return to the Course index
previous | next
Material on this website should be used for Educational or Self-Study Purposes Only
Copyright © 2001 - 2026 David W. A. Bourne (david@boomer.org)
 | A game to aid in interpreting Prescription Sig instructions See how many Sigs you can catch before you run out of lives |
|