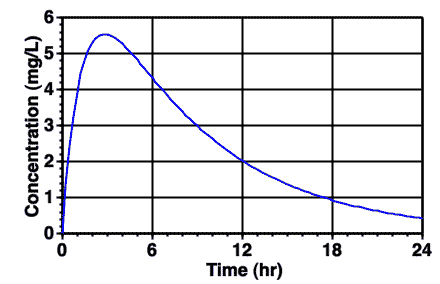
Figure 7.4.1 Typical Plot of Cp versus Time after Rectal Administration
return to the Course index
previous | next
Advantages:
By-pass liver - Some (but not all) of the veins draining the rectum lead directly to the general circulation thus by-passing the liver. Therefore there may be a reduced first-pass effect.
Useful - This route may be most useful for patients unable to take drugs orally or with younger children.
Disadvantages:
Erratic absorption - Drug absorption from a supppository is often incomplete and erratic. However for some drugs it is quite useful. There is research being conducted to look at methods of improving the extent and variability of rectal administration. Absorption from solutions used as an enema may be more reliable.
Not well accepted. May be some discomfort.

Figure 7.4.1 Typical Plot of Cp versus Time after Rectal Administration
return to the Course index
previous | next
Material on this website should be used for Educational or Self-Study Purposes Only
Copyright © 2001 - 2026 David W. A. Bourne (david@boomer.org)
 |
The Book Pharmacokinetics This Course in ePub format |
 |