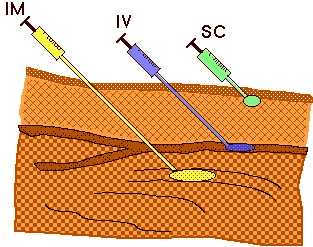
Figure 7.5.1 Showing IV, IM, and SC Injection
return to the Course index
previous | next

Figure 7.5.1 Showing IV, IM, and SC Injection
Advantages:
Rapid - A quick response is possible. Plasma concentration can be precisely controlled using IV infusion administration.
Total dose - The whole dose is delivered to the blood stream. That is the bioavailability is generally considered to 100% after IV administration. Larger doses may be given by IV infusion over an extended time. Poorly soluble drugs may be given in a larger volume over an extended time period.
Veins relatively insensitive - to irritation by irritant drugs at higher concentration in dosage forms.
Disadvantages:
Suitable vein - It may be difficult to find a suitable vein. There may be some tissue damage at the site of injection.
Maybe toxic - Because of the rapid response, toxicity can be a problem with rapid drug administrations. For drugs where this is a particular problem the dose should be given as an infusion, monitoring for toxicity.
Requires trained personnel - Trained personnel are required to give intravenous injections.
Expensive - Sterility, pyrogen testing and larger volume of solvent means greater cost for preparation, transport and storage.
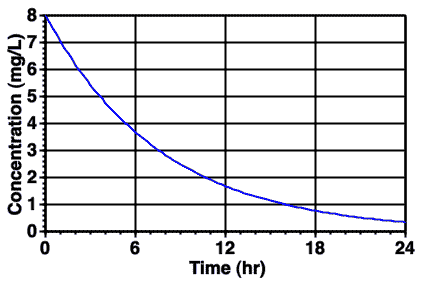
Figure 7.5.2 Typical Plot of Cp versus Time after IV Bolus Administration
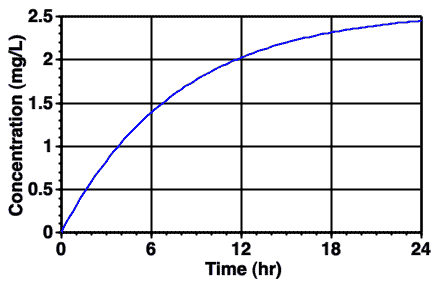
Figure 7.5.3 Typical Plot of Cp versus Time during an IV Infusion Administration
return to the Course index
previous | next
Material on this website should be used for Educational or Self-Study Purposes Only
Copyright © 2001 - 2026 David W. A. Bourne (david@boomer.org)
 | A tvOS app which presents a collection of video tutorials related to Basic Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacy Math |
|