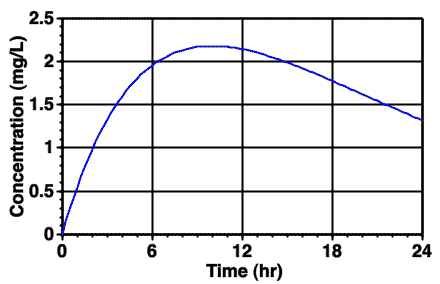
Figure 7.6.1 Typical Plot of Cp versus Time after Subcutaneous Administration
return to the Course index
previous | next
Advantages:
Can be given by patient, e.g. in the case of insulin.
Absorption can be fast from aqueous solution but slower with depot formulations. Absorption is usually complete. Improved by massage or heat. Vasoconstrictor may be added to reduce the absorption of a local anesthetic agent, thereby prolonging its effect at the site of interest.
Disadvantages:
Can be painful. Finding suitable sites for repeat injection can be a problem.
Irritant drugs can cause local tissue damage.
Maximum of 2 ml injection thus often small doses limit use.

Figure 7.6.1 Typical Plot of Cp versus Time after Subcutaneous Administration
return to the Course index
previous | next
Material on this website should be used for Educational or Self-Study Purposes Only
Copyright © 2001 - 2026 David W. A. Bourne (david@boomer.org)
 | Pharmacy Math Part Two A selection of Pharmacy Math Problems |
 |