Chapter 23
Pharmaceutical Analysis
return to the Course index
previous | next
Radioimmunoassay (RIA)
RIA involves the separation of the drug using the specificity of antibody - antigen binding and quantitation using radioactivity.
Components of RIA Assay Kit
- Drug
- Antibody
- Labelled Drug
General Procedure for Performing a RIA Analysis
- Mix sample containing drug with fixed quantity of labelled drug and antibody
- Allow to equilibrate - incubate
- Separate drug bound to antibody from unbound drug
- Charcoal adsorption of antibody (and bound drug)
- Antibody - antibody binding precipitates bound drug
- Antibody bonded to container
- Measure radioactivity associated with bound labelled drug
- low drug concentration means more bound radioactivity and higher measurement
- high drug concentration means less bound radioactivity and lower measurement
- Determine standard curve
- Non-linear plot of radioactivity versus concentration
- Logit-log concentration plot is linear
A Blank and Three Standard Samples

Fig 3.7.1 RIA before and after Incubation - Blank and Three Standard Samples
Table 23.7.1 Bound and Free Drug Concentrations
| Drug |
Bound |
Y'
B/Bo |
Labeled
Drug, B |
Drug |
| 0 | 6 (Bo) | 0 | - |
| 3 | 4 | 2 | 0.667 |
| 6 | 3 | 3 | 0.5 |
| 12 | 2 | 4 | 0.333 |
| 30 | 1 | 5 | 0.167 |
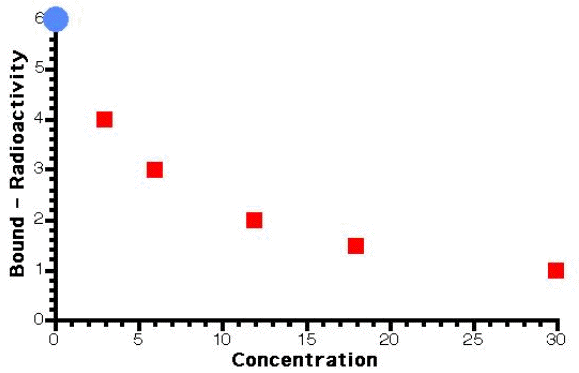
Fig 23.7.2 Plot of Bound versus Total Drug Concentration
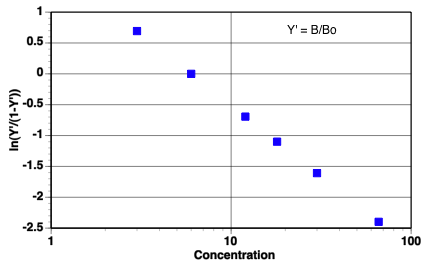
Fig 23.7.3 Logit versus Log Total C Plot
return to the Course index
This page was last modified: Sunday, 28th Jul 2024 at 5:07 pm
Privacy Statement - 25 May 2018
Material on this website should be used for Educational or Self-Study Purposes Only
Copyright © 2001 - 2026 David W. A. Bourne (david@boomer.org)
 | Drug Structures
A game to aid recognizing drug structures
See how many structures you can name before you run out of lives |

|




