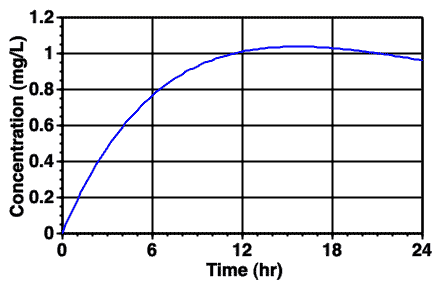
Figure 7.9.1 Typical Plot of Cp versus Time after Topical Administration
return to the Course index
previous | next
Systemic effect - e.g., nitroglycerin ointment.
Generally absorption is quite slow. Absorption through the skin especially via cuts and abrasions or from sites were the skin is quite thin can be quite marked. This can be a real problem in handling toxic materials in the laboratory or pharmacy. This can also be a serious problem with garden chemicals.
An occlusive dressing may be used to improve absorption.
Transdermal patches can provide prolonged or controlled (iontophoresis) drug delivery.
There may be some skin irritation. Drug absorption will vary by site of administration, skin condition, age and gender.
Systemic absorption (transdermal) is better with low dose, low MWt, lipid soluble drugs.

Figure 7.9.1 Typical Plot of Cp versus Time after Topical Administration
Examples of drugs delivered by the transdermal route include estradiol, fentanyl, nicotine (various forms), nifedipine and nitroglycerin.
return to the Course index
previous | next
Material on this website should be used for Educational or Self-Study Purposes Only
Copyright © 2001 - 2026 David W. A. Bourne (david@boomer.org)
 | An iPhone app that facilitates the geotagging of Bird Count stops and the return to the same stops during the next and subsequent Bird Count sessions |
|