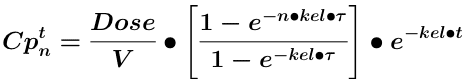
Equation 14.6.1 Cp at time, t, after the nth IV Bolus Dose
General Equation
return to the Course index
previous | next
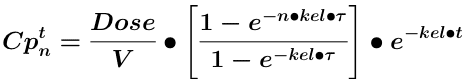
Equation 14.6.1 Cp at time, t, after the nth IV Bolus Dose
General Equation
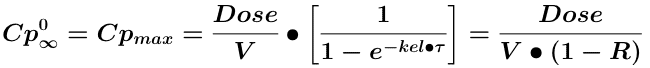
Equation 14.6.2 Cp Immediately after Many Doses
Equation 14.6.3 Cp Immediately before Many Doses
An example may be helpful: t1/2 = 4 hr; IV dose 100 mg every 6 hours; V = 10 liter
What are the Cpmax and Cpmin values when the plateau values are reached
therefore
therefore the plasma concentration will fluctuate between 15.5 and 5.48 mg/liter
during each dosing interval when the plateau is reached.
Equation 14.6.4 Accumulation Factor
It is interesting to note that if the dose is given every drug elimination half-life the accumulation factor is two since R equal to e-kel • τ equals one half.
If dosing every half-life Cpmax is twice the Cp01 value and Cpmin is equal to the Cp01 value.
For the example above R is equal to 0.354 and the accumulation factor can be calculated.
To complete the example above we can calculate the plasma concentration at any time following multiple IV bolus administration (using Equation 14.5.11 on the previous page) AND we can calculate the Cpmax and Cpmin values (using Equation 14.6.2 and 14.6.3 above).
Figure 14.6.1 Plot of Cp versus Time showing Time to Approach
Click on the figure to view the interactive graph



![]()


Accumulation Factor
In Equation 14.6.2 the ratio, Dose/V represents the initial concentration after the first dose. Thus the ratio between the highest, initial concentration at steady state, Cpmax and the highest concentration after the first dose, Cp01 can be expressed as the ratio.




50% of Plateau during Multiple Dose Regimen
Time to Cpmax/Cpmin
Just as in the case of a continuous infusion it takes some time to get to the plateau where the concentrations vary between Cpmax and Cpmin during each dosing interval. As before, it can be shown that the time to reach a certain fraction of the plateau
concentration is dependent on the drug elimination half-life only, much the same as for the approach to steady state during an IV infusion. Thus we may again have a problem with an excessive time required to reach the plateau. Administration of a loading dose will achieve steady state concentrations rapidly.
Practice problems involving Cpmax and Cpmin at steady state after uniform multiple dose IV bolus doses.
Another practice problems involving Cpmax and Cpmin at steady state after uniform multiple dose IV bolus doses.
A third practice problems involving Cpmax and Cpmin at steady state after uniform multiple dose IV bolus doses.
Other practice problems involving the calculation of Cp at three times during a uniform dosing interval with Linear or Semi-log graphical answers or calculation of Cp at three times during a non-uniform dosing interval with Linear or Semi-log graphical answers.
Material on this website should be used for Educational or Self-Study Purposes Only
Copyright © 2001 - 2026 David W. A. Bourne (david@boomer.org)
 | A game to aid in interpreting Prescription Sig instructions See how many Sigs you can catch before you run out of lives |
|